Introduction
Enter the realm of Dimethocaine (DMC, larocaine) – a compound with a structure resembling procaine, known for its stimulating effects akin to cocaine. Often referred to as DMC or larocaine, this compound holds a unique position as a legal replacement for cocaine in certain countries, acknowledged by the European Monitoring Centre for Drugs and Drug Addiction (EMCDDA). Let’s explore further into what dimethocaine offers and how it’s used.
Experience the Potential: Dimethocaine, also known as DMC or Larocaine, mirrors cocaine’s actions as a local anesthetic. With a potency akin to cocaine, it completely halts dopamine uptake in rat striatal synaptosomes, closely mirroring cocaine’s impact. Demonstrating a dose-dependent substitution for cocaine in drug discrimination tests in rats and rhesus monkeys, this product is exclusively meant for forensic and research applications.
Understanding Dimethocaine
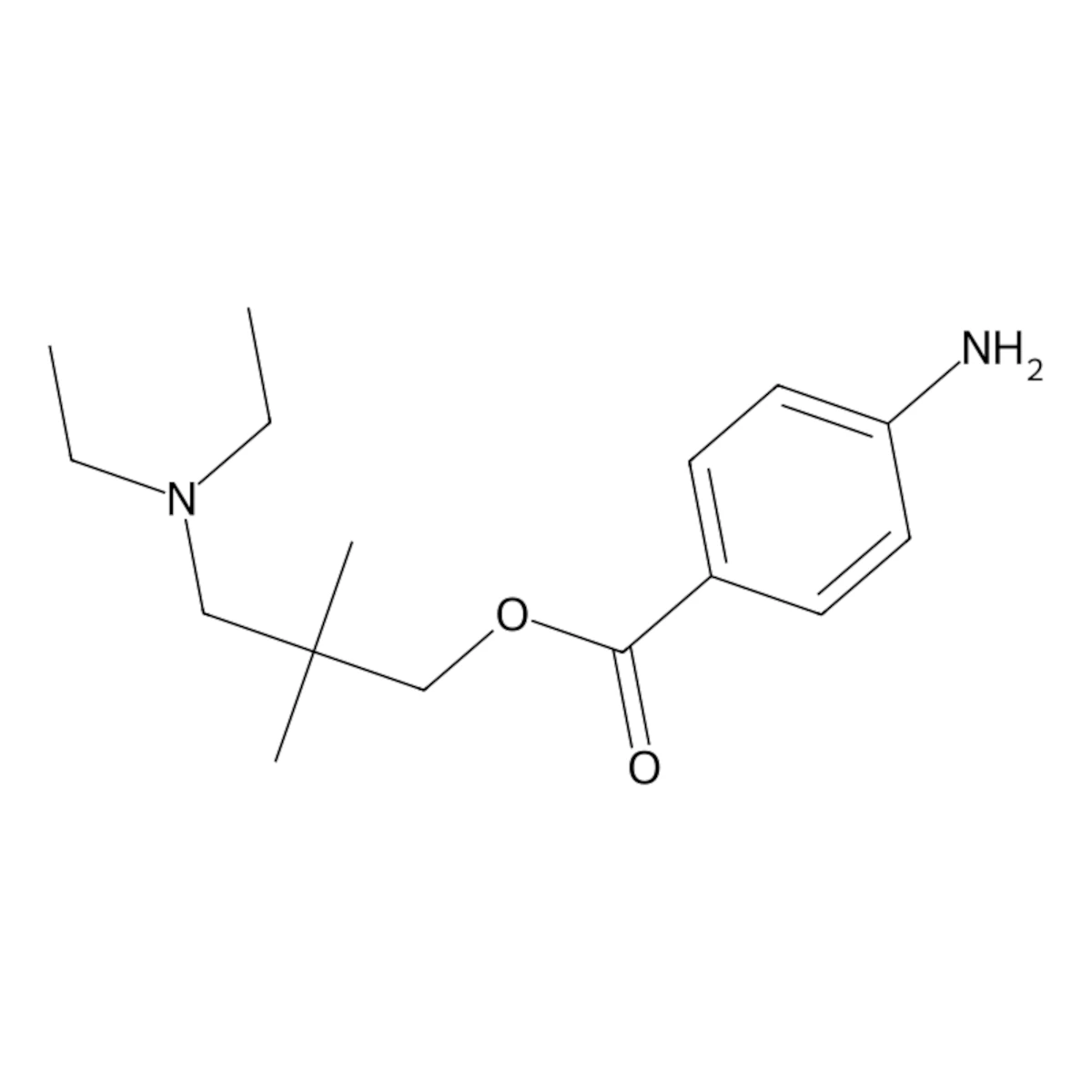
Dimethocaine (DMC, larocaine), an ester of 4-aminobenzoic acid, shares structural similarities with procaine. This compound presents itself as a powder at room temperature, eliciting a stimulation akin to cocaine. It influences the brain’s reward pathway, sparking tendencies toward addiction.
Legality and Purpose
Despite its resemblance to cocaine, Dimethocaine (DMC, larocaine) serves as a legal alternative and is categorized by EMCDDA as a “synthetic cocaine derivative.” Originally utilized as an anesthetic in dentistry, ophthalmology, and otolaryngology during the 1930s, it is now primarily intended for forensic and research applications due to its potential for abuse.
Exploring Resiniferatoxin’s Biological Activity
Shifting focus to resiniferatoxin, a compound with astounding heat units, ranking at 16 billion on the Scoville scale, surpassing the heat intensity of pure capsaicin by 500 to 1000 times. This compound triggers the transient vanilloid receptor 1 in particular sensory neurons that play a role in transmitting physical pain, known as nociception.
Mechanism of Action
Resiniferatoxin’s interaction with TRPV1, an ion channel on sensory neuron membranes, induces cation permeability, notably calcium influx. This rush of ions causes the neurons to depolarize, imitating signals similar to those of tissue damage or a burning sensation. Subsequently, desensitization and analgesia follow, partly due to nerve ending demise from calcium overload.
The Historical Context of Dimethocaine
Originally synthesized by Hoffmann-La Roche in 1930 and marketed as “larocaine,” dimethocaine gained traction in the US during the 1930s for its anesthetic properties, akin to cocaine and procaine. However, its psychoactive effects and addiction potential led to its removal from the market in the 1940s. Presently, it’s unlawfully employed for its psychoactive effects, sold as a surrogate for cocaine, bypassing legal restrictions.
This revised content elaborates on the characteristics, historical background, and uses of dimethocaine and resiniferatoxin, adhering to a conversational style while incorporating headings and subheadings for enhanced readability.
General Information
| Name | Information |
|---|---|
| CAS Number | 94-15-5 |
| Product Name | Dimethocaine |
| IUPAC Name | [3-(diethylamino)-2,2-dimethylpropyl] 4-aminobenzoate |
| Molecular Formula | C16H26N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 278.39 g/mol |
| InChI | InChI=1S/C16H26N2O2/c1-5-18(6-2)11-16(3,4)12-20-15(19)13-7-9-14(17)10-8-13/h7-10H,5-6,11-12,17H2,1-4H3 |
| InChI Key | OWQIUQKMMPDHQQ-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | CCN(CC)CC(C)(C)COC(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)N |
| Solubility | Soluble in DMSO |
| Synonyms | 3-(diethylamino)-2,2-dimethylpropyl 4-aminobenzoate, dimethocaine, dimethocaine hydrochloride |
| Canonical SMILES | CCN(CC)CC(C)(C)COC(=O)C1=CC=C(C=C1)N |
| Description | The compound Dimethocaine boasts an exact mass of 278.1994, while its complexity rating remains undisclosed. It demonstrates solubility in DMSO. Submitted to the National Cancer Institute (NCI) for extensive evaluation, it holds the NSC number 68927 under the category of Chemicals and Drugs – Organic Chemicals – Amines – Amino Alcohols – Propanolamines within Medical Subject Headings (MeSH). Categorized as a benzoate ester in the ChEBI Ontology tree, it requires storage in dry, dark conditions at 0-4°C for short-term use or -20°C for extended preservation (months to years). |
Specification
| Name | Information |
|---|---|
| Purity | >98% (or refer to the Certificate of Analysis) |
| XLogP3 | 3.1 |
| Exact Mass | 278.1994 |
Others
| Name | Information |
|---|---|
| Appearance | Solid powder |
| Storage | Dry, dark and at 0 – 4 C for short term (days to weeks) or -20 C for long term (months to years). |
| UNII | R3L4A6GOWZ |
| Related CAS | 553-63-9 (hydrochloride) |
| MeSH Pharmacological Classification | Anesthetics, Local |
| Other CAS | 94-15-5 |
| Wikipedia | Dimethocaine |
| Dates | Modify: 2023-08-15 |